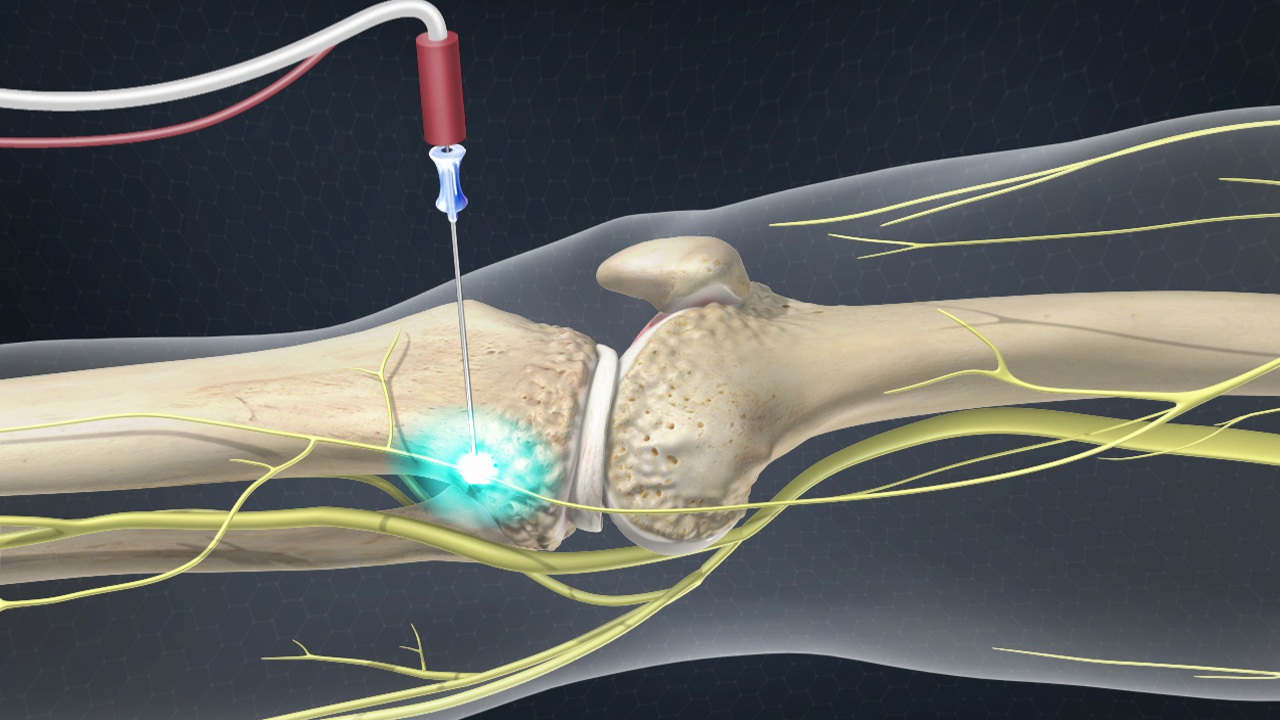
Cryoablation: An overview of evidence and clinical use
Cryoablation is a technique using extreme cold for nerve and tissue management, particularly in pain relief, with established clinical applications and evidence.
Highlights
- ❄️ Cryoablation Mechanism: Utilizes extreme cold to target and ablate tissue or nerves.
- 📊 Clinical Applications: Effective for both acute and chronic pain management.
- 🔍 Efficacy Evidence: Numerous studies support its use across various pain conditions.
- 🚑 Case Studies: Real-world examples illustrate successful cryoablation outcomes.
- ⚖️ Risk Considerations: Awareness of potential complications is crucial in decision-making.
- 📈 Comparison with RFA: Differentiates cryoablation from radiofrequency ablation in terms of application.
- 🔬 Future Potential: Promising opportunities for innovative uses in pain management.
Key Insights
-
❄️ Mechanism of Action: Cryoablation induces a conduction block in nerves by creating ice crystals, leading to long-lasting pain relief. This reversible axonal injury allows for a gradual recovery of nerve function, making it distinct from permanent ablative techniques.
-
🩺 Diverse Applications: The technique is versatile, effectively treating conditions like intercostal neuralgia, post-surgical pain, and neuropathic pain, highlighting its role in comprehensive pain management strategies.
-
📊 Evidence-Based Support: Various studies demonstrate cryoablation’s effectiveness, especially in post-operative pain and chronic conditions, reinforcing its clinical relevance and utility.
-
🧪 Case Studies: Real-world applications showcased positive outcomes, with patients experiencing significant pain relief and improved quality of life, underscoring the practical benefits of the procedure.
-
⚠️ Risk Management: Potential risks include nerve damage and pain recurrence, emphasizing the importance of patient selection and careful procedure execution to minimize complications.
-
🔄 Cryo vs. RFA: While both techniques serve to manage pain, cryoablation is preferred for sensory nerve targeting, as it avoids the complications associated with permanent nerve damage seen in traditional radiofrequency ablation.
-
🔭 Innovative Future Uses: The exploration of cryoablation for other applications, such as spasticity management, indicates its potential to evolve and expand within pain management and neurological care.
Leave Comment